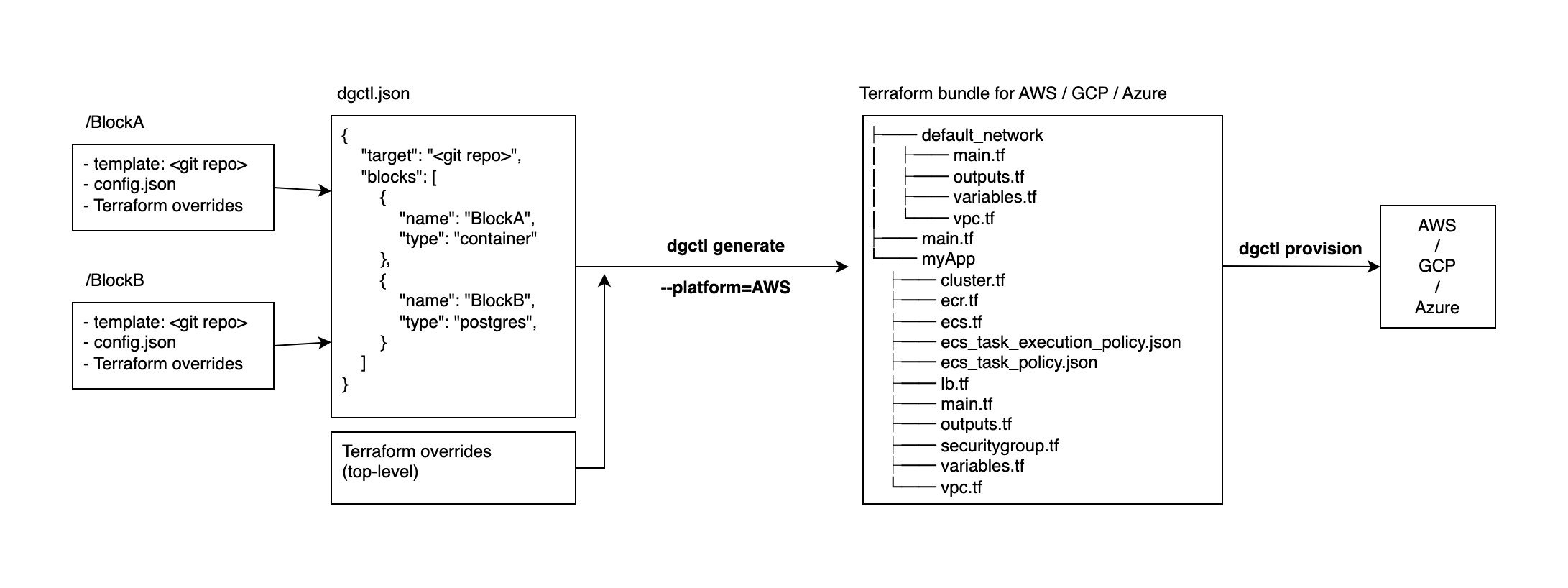
How it works
Digger stores a high-level, cloud-agnostic representation of your stack in the dgctl.json file.
The dgctl.json file has a list of blocks. Each block represents a piece of infrastructure and produces Terraform for its provisioning.
You can change behaviour of blocks by either changing their template (target) to a different repo, or by adding your custom Terraform into the overrides folder in the block's directory.
FAQ
Q: Why dgctl.json and per-block config.json are split?
A: Single large config file quickly becomes unmanageable. Example: serverless.yml
TODO: figure out the right abstraction for things like CloudWatch that spans across multiple blocks. For now it is part of the block but that's not clean.
Last updated